How to design a website for better (and quality) SEO traffic
Getting more high-quality organic traffic is a holy grail for any business looking to grow their revenue. After all, more traffic means more conversions and ultimately a bigger bottom line. However, for many small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs), the cost of traffic generation through paid channels like pay-per-click (PPC) advertising or sponsored content can be a limiting factor.
Rocket-power blog post SEO with easy-to-implement strategies. Download the Blog SEO Checklist right now and make a bigger impact for your clients.
That's where search engine optimization (SEO) comes in. While optimizing for organic traffic is a long-term project, it can pay off significantly in the long run by driving unpaid visitors to a website. Link-building gets a lot of attention in the world of SEO, but web design also plays a critical role in helping sites land at the top of their relevant search engine results pages (SERPs). By optimizing website design and content for search engines, you can attract more organic SEO traffic without having to shell out marketing dollars for each visit. In this article, we'll share five web design tips that can help you improve your SEO and drive more conversion-ready traffic to your website.
Table of Contents
- What is traffic in SEO? Organic vs. non-organic
- Why does SEO traffic matter for website success?
- Understanding on-page and off-page SEO
- Web design tips for SEO traffic generation
- How Vendasta can help
- Frequently asked questions
What is traffic in SEO? Organic vs. non-organic
Organic traffic refers to website visitors that arrive through unpaid channels, typically search engines. Non-organic traffic encompasses visitors who reach a site through a paid channel. Both types of traffic generation are valuable to SMBs, and the best digital marketing strategies usually combine efforts to drive both organic and non-organic traffic.
Let’s dig into what exactly is included in each category of web traffic.
Organic traffic
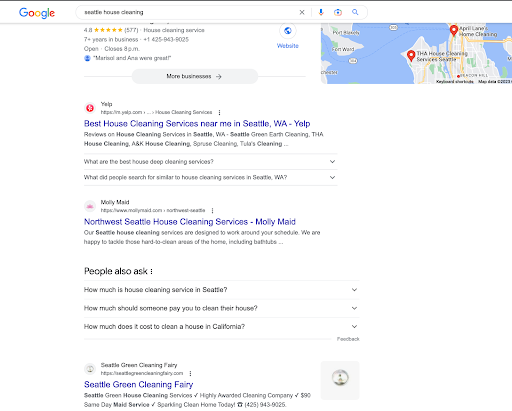
Organic search results, the drivers of organic traffic, are the listings that appear in SERPs without being paid for by advertisers. Here’s an example of the top 3 organic search results for the query “Seattle house cleaning”:
These unpaid results for Yelp, Molly Maid, and Seattle Green Cleaning Fairy appear just below paid ads and Google’s local 3-pack. Google determines which websites are most relevant to the user's search query and displays them without the website having to pay to be included. In this sense, organic traffic generation is “free”, although businesses often invest considerably in SEO that helps them land in one of these coveted top spots.
The local 3-pack, a box of 3 suggested businesses matching the search query for location-based searches such as this one, is another source of organic traffic. Businesses don’t pay to appear in the local 3-pack, but instead maintain their websites, Google Business Profile (GBP), and other local listings in hopes of gaining a 3-pack spot.
Businesses earn this unpaid SEO traffic through optimizations like the ones we’ll discuss in just a moment. These signal to Google that a website is relevant, trustworthy, and high-quality enough to meet the search query.
Non-organic traffic
Non-organic traffic, also known as paid traffic, is any traffic that a website receives because they paid to get in front of their target audience. Any traffic flowing to Mollymaid’s website by clicking on their ad on this SERP would constitute non-organic traffic, while those scrolling further down the page and clicking on their organic listing would count as organic SEO traffic.
This type of traffic is generated through paid advertising like PPC ads, display ads, or social media ads. The amount that businesses pay for each non-organic visitor depends on variables like the number of clicks, impressions, or conversions generated by their ad campaigns.
Key differences
The primary difference between organic and non-organic traffic is how the traffic is generated. Organic traffic is generated naturally through a search engine's algorithm, while non-organic traffic is generated through paid advertising.
Organic traffic is not paid for directly, while businesses need to pay for every non-organic visitor. Often, organic traffic can be more high-quality than non-organic traffic because the leads are actively searching for the product or service in question, and may be more motivated to convert.
Organic SEO traffic takes time to build, because it takes a while for Google’s algorithm to index changes and reshuffle the order in which organic search results appear. However, this also makes organic traffic more durable. In other words, SEO efforts made today can pay off for months, or even years, to come. In contrast, non-organic traffic is only generated as long as the paid advertising campaigns are active. Once the campaigns stop running, the traffic also stops.
Why does SEO traffic matter for website success?
SEO traffic drives website success because it drives high-quality prospects, helps to build trust with audiences, and provides a sustainable source of traffic over the long term. This isn’t to say that there’s no place for paid ads—the best digital agencies help their clients maximize ROI by combining both paid and SEO strategies—but neglecting SEO traffic tracking can seriously hinder a business’s success.
- It attracts more high-quality traffic. When a website’s design and content are optimized for search engines, it’s more likely to appear at the top of SERPs when users search for relevant keywords. Organic traffic is made up of users who are actively searching for products or services related to the website's offerings, making them more likely to convert into customers.
- It establishes a business as trustworthy and credible. When a website appears at the top of SERPs, it is perceived as more trustworthy by users. The higher a website's credibility, the more likely it is to attract high-quality traffic and generate conversions.
- It can be sustained long-term. Unlike non-organic traffic, which is generated through paid advertising campaigns that require ongoing investment, organic traffic can continue to generate leads and conversions even after the initial optimization work has been completed. By continuing to produce high-quality content and optimizing for search engines, businesses can maintain their search engine rankings and continue to attract high-quality traffic over time.
Understanding on-page and off-page SEO
On-page and off-page SEO refer to two types of optimization that influence website ranking in search engines. On-page SEO takes place on the website itself, while off-page SEO takes place elsewhere on the internet but still serves to boost a website’s performance on SERPs.
On-page SEO
On-page SEO is the optimization of website design, content, and HTML source code elements on a page-by-page basis. This includes optimizing title tags, meta descriptions, headers, image tags, and URLs. On-page optimization also includes ensuring that content is high-quality, original, relevant, and engaging to target audiences.
Websites that are optimized for on-page SEO tend to provide a better user experience and are more likely to attract high-quality traffic. The same on-page optimizations that help a website perform well with Google and other search engine algorithms also tend to improve it for real human audiences.
Why? Because the goal of Google’s search engine is to provide value to users by serving them the best, most relevant results for their queries. Optimizing for Google ultimately means optimizing for the real users that make up an audience.
Off-page SEO
Off-page SEO includes activities that are performed outside the website to improve its search engine ranking. This includes link building, social media marketing, influencer outreach, podcasting, guest posts, and other marketing strategies that drive traffic and increase the visibility of the website. Off-page optimization demonstrates to search algorithms that the website is authoritative, credible, and trustworthy.
Off-page SEO activities generally encourage conversation and engagement about a business beyond its own website. The more Google’s crawlers index these off-site mentions, the greater the signal is that a website is getting buzz, and therefore must be interesting and relevant.
The result? Improved SEO rankings.
Impact on rankings
Both on-page and off-page SEO play a key role in improving website rankings on SERPs. On-page SEO helps search engines understand the content of a website and how it is relevant to user search queries. Meanwhile, off-page SEO helps search engines gauge the popularity and authority of a website. In addition to helping boost rankings, off-page SEO can drive more traffic to a website through links and mentions.
Websites with a combination of excellent on-page optimizations and a high number of quality backlinks from authoritative sources tend to rank higher in search engine results. As is so often the case in digital marketing, a robust strategy that combines multiple approaches—in this case, on-page and off-page optimizations—is most likely to deliver great results.
Web design tips for SEO traffic generation
To ace your clients’ on-page SEO, use this list of web design tips as a checklist. These optimizations focus on the on-page side of SEO. Coupled with a great off-page strategy, they can help businesses secure a spot at the top of the SERPs.
1. Optimize the website structure
Website structure refers to the way a site’s pages are organized and connected. It can be thought of as a roadmap that guides users and search engines through the website's content. The structure of a website can have a significant impact on its SEO performance and overall success.
Why it matters for SEO traffic
Google’s bots, also known as crawlers, navigate through a website in much the same way that a human user might, to gather information about what that site contains. This data plays a major role in determining which SERPs a website will appear in.
Since a well-structured site is most likely to be properly indexed, it’s also more likely to be discoverable in search, driving more traffic. Conversely, even if a website has excellent content, a poorly designed website structure can mean that Google’s algorithm doesn’t properly understand its relevance. This limits its chances of appearing in search results.
Website structure optimization tips
Let’s take a closer look at how the elements of website structure can be optimized for SEO traffic generation.
- Site Navigation. The navigation of a website should be designed to be simple and intuitive, making it easy for users and search engines alike to understand the structure of the website. Navigation should be designed to provide a clear hierarchy of content, with the most important pages at the top level of the navigation.
- URL Structure. URLs should be designed to be clear, concise, and descriptive of the page's content. A clear and descriptive URL can help users and search engines understand what the page will be about. A consistent URL system should be used across the website, with a clear hierarchy that reflects the structure of the website's content.
- Internal Linking. Internal links help to establish a website's hierarchy and provide context about a website's content. Internal linking can also help to distribute link equity throughout the website, which can help to improve the search engine ranking of individual pages.
2. Optimize on-page elements
Website on-page elements include various components of a webpage that can be optimized to improve its SEO performance. Elements included in this category are title tags, image alt text, and content optimizations.
Why it matters for SEO traffic
These elements boost SEO performance by clearly organizing webpage content, helping both Google’s bots and real users quickly and easily interpret information. You can think of on-page elements as the next level of organization after website structure. Website structure organizes the website as a whole, while on-page elements organize each individual page on a site.
On-page elements optimization tips
Each of these elements should be audited and optimized to make sure they accurately convey the information contained on the page:
- Title Tags. Title tags are displayed in the browser's title bar and should provide a brief and concise description of the webpage's content. They provide search engines with a clear cue of what the webpage contains so that it has a better chance of appearing in the appropriate, relevant SERPs.
- Meta Descriptions. Meta descriptions don’t generally appear on a webpage itself, but rather in the page’s source code and in SERPs below the title tag. Best practices for meta descriptions include keeping them 155 or fewer characters, incorporating a focus keyword, and enticing readers to click through and read more.
- Headers. Headers and sub-heads provide structure to the content of a webpage. Use them to break up the content into small, readable sections and to provide context to users and search engines.
- Image Alt Text. Image alt text provides a description of an image on a webpage and is displayed in place of an image if the image cannot be loaded. Incorporate keywords in alt text when appropriate, and keep the text brief and descriptive.
- Content Optimization. Content optimization includes identifying relevant keywords and incorporating them into content, using headers, bullet points, and lists to improve readability, and interlinking with other relevant pages. Ideally, a hurried reader should be able to scan your content and get the gist at a glance.
3. Publish relevant, authoritative content
Content, such as blog posts or product guides, should be relevant to the business’s target audience and reflect the subject area in which they have an authoritative voice. In other words, a marketing agency will be best off publishing high-quality marketing content rather than, say, legal content.
Why it matters for SEO traffic
The old marketing adage that content is king may have been repeated to death by now, but there’s a good reason for this: it’s true. The primacy of quality content when it comes to SEO isn’t going to change any time soon.
Google gathers a range of information from website content to determine if it is relevant and authoritative for a given SERP, and the more excellent content a website has, the greater its chances of performing well in search results. There is also a direct effect of traffic in SEO: when a page gets more traffic, which can be generated by quality content, a feedback loop is created. Google gets a signal that the website is popular and authoritative, which further improves SEO rankings.
Content publication tips
As a general rule, creating the best possible content for an audience of human readers will also help drive SEO traffic. Google’s own guidelines advise users to “create helpful, reliable, people-first content” to climb the SERPs. However, there are some useful tips to keep in mind during content creation that can maximize performance in search.
- Keep E-E-A-T in mind. Google aims to promote content that demonstrates expertise, experience, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness (E-E-A-T). Content that showcases these qualities tends to have better visibility in search results pages, leading to more organic SEO traffic.
- Research relevant keywords. Keyword research involves identifying the keywords and phrases that users are searching for in relation to a website's topic or industry. By incorporating these keywords into the website's content, headers, and meta descriptions, SMBs can optimize their content for better search engine rankings.
- Update content regularly. Websites that are updated frequently tend to have better search engine rankings than those that are not regularly updated because they contain the most recent information and can be continually optimized with improved keywords, headings, and other on-page elements. Blog traffic can be maximized over time by further optimizing already well-performing posts.
- Avoiding keyword stuffing. Keyword stuffing refers to the practice of using keywords excessively in an attempt to manipulate search engine rankings. This practice is against Google's guidelines and can result in penalties and lower SEO traffic. It can also be annoying to read, damaging the user experience.
- Track performance. Tools like Google’s Search Console Insights make it easy to see important metrics for well-performing content, so you can identify what’s working and repeat it.
4. Ensure mobile responsiveness
Mobile responsiveness in web design refers to how a website adapts and adjusts to different screen sizes and devices, such as smartphones and tablets. A mobile-responsive website is designed to provide an optimal user experience on all devices, regardless of the screen size, manufacturer, or browser being used.
This is achieved through a combination of web design and coding techniques, such as using fluid layouts, flexible images, and media queries. These techniques allow the website to adjust its layout and content to fit the screen size of the device, while still maintaining its visual appeal and functionality.
Why it matters for SEO traffic
In the past, web design primarily focused on creating websites that were optimized for desktop and laptop screens. However, with the growing use of mobile devices to access the internet, mobile responsiveness has become an unignorable component of modern web design.
Not only does a mobile-responsive website provide a great user experience to anyone regardless of their device, but responsiveness is also a direct ranking factor for Google. With over 60% of Google search traffic originating from mobile devices, it makes sense to prioritize websites that don’t lose functionality on mobile screens (Statista).
Tips for mobile-responsive web design
- Consider a mobile-first approach. Many web designers begin with a desktop layout out of habit, but given the way we engage with screens today, it can be a better approach to start with a mobile layout and work from there.
- Use responsive templates. These days, a significant number of websites are created at least in part using page builders or templates. Starting with a template that is already optimized for responsiveness takes the guesswork out of the design process and ensures that every page on the site is mobile-friendly.
- Optimize images for mobile. Mobile devices typically have smaller screens and are more frequently used on slower internet connections. Image optimization can be achieved by compressing images, reducing their file size, and using images that look good on smaller screens.
- Use mobile-friendly fonts. Some fonts can be difficult to read on smaller screens, so it's important to use those that are easy to read on mobile devices. Sans-serif fonts are typically easier to read on mobile devices than serif fonts.
- Simplify navigation. Large, clunky menus can be difficult to use on smaller mobile screens. Simplifying navigation can make it easier for users to find what they are looking for. It’s not uncommon for websites to have different navigations for desktop and mobile viewing.
- Keep forms simple. Filling out forms on a mobile device can be more cumbersome than on a desktop, so it's best to keep them simple and easy to complete. This can be achieved by reducing the number of fields, enabling autofill options, and avoiding complex validation rules.
- Use mobile-friendly buttons. Buttons should be large enough to tap on a mobile device and should be positioned in a way that is easy to access. Use high-contrast colors to maximize visibility on smaller screens.
5. Improve page load speed
Page load speed refers to the amount of time it takes for a webpage to fully load in a user's web browser. It plays an important role in website performance and user experience since nearly half of users expect a webpage to load in 2 seconds or less.
Page load speed can be impacted by a number of factors, including the size of the webpage, the number of requests made by the webpage, the quality of the web hosting service, and the user's internet connection speed.
Why it matters for SEO traffic
Page load speed is one of Google’s direct ranking factors, meaning its algorithm is more likely to prioritize pages that load quickly.
Slow-loading pages pose a serious risk to SEO traffic, because even if a user clicks on a link to a website, the likelihood of them bouncing increases with every extra second of page load time. Going from 1-3 seconds increases the bounce rate by over 30% (Think with Google). This means that even if a website does everything right in terms of optimizations, and lands at the top of Google’s SERPs, it can lose valuable conversions—and revenue—if page speed isn’t optimized.
Tips for page speed optimization
Since every second counts when it comes to page speed, addressing as many optimizations as possible can have a meaningful impact on a website’s revenue.
- Minimize file sizes. One of the most effective ways to improve page load speed is to minimize the size of files, including HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. This can be achieved by removing unnecessary code, minimizing whitespace, removing unused plugins, and compressing files.
- Enable compression. Compression can help to reduce the size of files and improve page load speed. Gzip compression is a popular method for compressing files and reducing the amount of data that needs to be transferred.
- Optimize images. Images are often the most slow-loading elements in web design, and they can negatively impact page load speeds. Compressing images, reducing their file size, and using lighter image formats can help speed up load times.
- Leverage caching. Caching can help to improve page load speed by storing frequently accessed data and serving it quickly to users. This can be achieved by using browser caching and server-side caching.
- Reduce server response time. Slow server response time can negatively impact page load speed. This can be improved by choosing a reputable hosting service and using a solution to manage bot traffic.
- Use a content delivery network (CDN). CDNs cache content and then serve it to users from servers that are close by. This can help to reduce page load speeds, especially for websites using more affordable shared hosting services.
- Keep it simple. While interactive elements and scroll effects can be fun, they don’t necessarily boost conversions, and they can drag down page load speeds. Use these effects sparingly.
How Vendasta can help
Whether you’re a website builder reseller or you sell complete web design services, Vendasta's Website Pro can help your business grow. This powerful tool includes an intuitive drag-and-drop page builder, world-class hosting and security from Google, and built-in e-commerce functionality. It can be used to create speedy, responsive, SEO-optimized websites with just a few clicks. The platform offers a wide range of templates across many popular verticals that can be customized to match the branding and unique needs of each of your clients. Plus, Website Pro integrates with a vast array of SEO tools and SEO traffic tracking software, enabling businesses to track performance and make data-driven decisions to improve SEO traffic over time.
Don’t have time to build websites in-house? Vendasta's white-label web design services can be used to create websites for clients at scale without the need to invest in in-house designers. Access a team of experienced web designers who can be there for you on-demand as you grow your website client list and continue to pitch websites to clients.
Sell more by bundling web design and SEO services to deliver value to your clients while boosting your revenue and customer lifetime value (LTV). Selling these services together enables you to generate a monthly revenue stream after the initial website build is complete, and by regularly reporting SEO insights and forecasting SEO traffic, you can demonstrate ongoing value to clients.
Frequently asked questions
How do I get traffic from SEO?
SEO drives traffic by helping websites appear at the top of Google’s search engine results pages. By appearing in search results, businesses can increase the organic traffic that they get without having to pay for ads.
Can I do SEO on my own?
Many SEO optimizations can be done on your own, and there are software solutions that can help. However, some aspects of SEO require technical knowledge or can be time-consuming to DIY, and professional insights can help create a robust SEO strategy.