How does Google Ads work?
The last few years have seen a significant increase in digital advertising streams, with digital ads soaring 35 percent to $189 billion in 2021 (IAB). That’s a $50 billion jump in a single year. It’s no surprise that more agencies, media companies, and resellers are now selling digital packages on top of radio, print, and TV ads. One of the most popular and most effective options for digital advertising is Google Ads. If you want to add just one digital ad stream for your clients, Google’s flagship platform is a solid choice. But how does Google Ads work?
Show REAL Google Ads value to your clients. Download the Digital Advertising ROI Template now.
Of course, apart from answering the question "How does Google Ads work?" you also need to know how to get the most out of this digital advertising solution to make it worthwhile for your clients.
We take a deeper look, answering not just “how does Google Ads work,” but making it clear how you can make Google Ads work for your clients.
What is Google Ads?
We’ll start with the basics: What is Google Ads?
The simplest answer is that Google Ads is a pay-per-click (PPC) advertising program. It’s similar to other digital ad platforms, like Facebook Ads or Amazon’s program. Pay per click quite literally means the advertiser pays only for the clicks received on its ads.
Google’s program is one of the most popular and most effective platforms available. It’s also one of the oldest. Google launched its PPC program back in 2000, two years after its search engine. At the time of its launch, the program was called “Google Adwords.” In 2018, Google rebranded the program as “Google Ads.”
The idea behind how to use Google Adwords was simple. Upload your ad creative, pick keywords to bid on, and set a maximum bid. If you have the winning bid, your ad appears on the Google search results page (SERP).
Over time, this process has become a bit more complex. These days, the Display Network serves over 2 million websites (Google). Other popular options that have been added since its inception include app campaigns and even YouTube ads.
The benefits of Google Ads
One of the most important benefits of Google Ads is broader reach. With different types of ad campaigns, your clients can get their ads in front of more people.
Display ads alone generate 180 million impressions every month (Solar Power World). Google itself handles more than 8 billion search queries every day (Earthweb). This offers a significant number of opportunities for ad placements!
What about goals like more sales? Google Ads has some pretty good stats on helping users reach growth and revenue goals.
- Google Ads have an average click-through-rate (CTR) of 3.17 percent (StoreGrowers)
- For customers who are ready to buy, Google Ads get 66 percent of clicks (Craig McConnel)
- Advertisers earn an average of $8 per every $1 spent on the platform (Google)
- More than 40 percent of people buy something they’ve seen on YouTube (Think with Google)
Surveys suggest customers do knowingly click on ads. The most common reason is that the ad matches what they want (Search Engine Land). That’s one reason Google Ads perform so well—it allows you to serve relevant ads to customers.
With traditional media streams, your targeting is often very broad. With Google Ads, you’re better able to target people who are already interested. With search ads, they are already looking for the products or services your clients offer.
That’s another benefit of Google Ads: they’re interactive. Users don’t need to wait to get home or drive to the store. They can click the ad and buy right then and there.
Other benefits of Google Ads include helping your clients land on Page 1 of the SERPs. Paid search is often a boon for those using SEO, especially for tough keywords. Even if your client’s site ranks organically, competitors’ ads are likely pushing them down the page.
How does Google Ads work: The basics
To benefit from Google Ads, you need to know the answer to the question: how does Google Ads work? You could just pick a keyword, set a maximum bid, and hope for the best. A deeper understanding of the question "How does Google Ads work?" will go a long way though.
This PPC platform is relatively easy to get started with. Set up your account, add a business name, and set up your first ad by uploading the creative.
Once you’ve done that, you’ll select keywords you want to bid on. Then you’ll set your maximum bid. When a user searches one of the keywords, Google compares the campaign against competitors.
If Google determines the ad placement costs less than your maximum bid, you get the placement. Google uses other factors, including quality scoring, to determine some placements. It’s not always a case of the highest bidder winning.
Bidding strategies
Advertisers can choose from three different bidding strategies for their campaigns. These are:
- Cost-per-click (CPC)
- Cost-per-mille (CPM)
- Cost-per-engagement (CPE)
CPC means you pay every time someone clicks on your ad. CPM is more traditional, in that you’ll pay per so many impressions. Impressions are a measure of how many times the ad appears in the SERPs or in placements on the Display Network. The cost is usually measured per 1,000 (which is where “mille” comes from).
CPE means you pay when a user takes a certain action. This could mean signing up for a newsletter or visiting a landing page. CPE tends to be more expensive than other bidding strategies for Google Ads.
There is a fourth strategy, known as cost-per-acquisition (CPA). While you can use CPA, Google Ads isn’t always the most effective with this option. It can cost a lot more in the long run.
Automated vs. manual bidding
You’ll also need to decide whether to use automated bidding or manual bidding for campaigns.
Manual bidding allows the advertiser to submit bids. It has some advantages, but it’s usually slower and increases the workload. Automated bidding is faster and has the advantage of not burdening teams. It also doesn’t have the same potential for human error.
Manual bidding is usually best if you don’t have a lot of data at hand. It takes time for the platform’s A.I. to learn which placements are best and how much to bid. Without data, it may bid on poor ad placements or spend your budget recklessly.
Types of ads
To understand "how does Google Ads work" it's good to understand that there are multiple types of ads. In addition to understanding bidding strategies for Google Ads, you need to know the different ad options. When Google first launched Adwords, search ads were the only choice. Today, advertisers can choose from five different ad campaign types:
- Search ads
- Display ads
- Shopping ads
- App campaigns
- YouTube ads
So how does Google Ads work? It depends on the type of ad you choose.
The type of ad campaign you want to run depends on the client. Where is their audience, and how can you best reach them? If they’re visiting websites on the Display Network, then display ads could be the right choice. If they watch a lot of YouTube videos, then YouTube campaigns might be a better option.
Google search ad example
Search ads are text ads that appear on the results page for any Google search. They usually appear at the top or bottom of the page. Text ads also appear on the Gmail platform.
Search ads include a headline and link. They also include a short description, as in the example below.
Google also offers Ad Extensions, which can increase the usefulness of the search ad. These extensions are Sitelink, Call, Location, Offer, and App.
Google display ad example
Display ads are the most common type of advertising on the internet. They appear as banner ads at the top, side, and bottom of many websites. Display ads also appear on some YouTube videos, often as a banner at the bottom of the video screen.
Display ads are flexible. They come in different shapes and sizes. Unlike search ads, they can contain more than text. In fact, display ads often include images, GIFs, or even video, as well as text.
Display ads can also include pop-up and pop-out ad placements. Here are a couple of Google display ad examples.
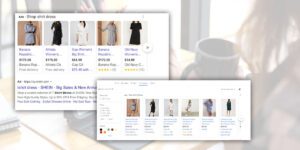
Google shopping ad example
Google shopping ads appear in two places. One is on the SERP, usually as part of a carousel at the top of the results page. They also appear under Google’s “Shopping” tab.
Shopping ads are helpful when users are looking for specific products or services. They include images of the product, as well as more information than a search ad. They include a link to the product, as well as pricing information. You can see them in the Google shopping ad example below.
Google Shopping isn’t as popular as a simple search. These ads can perform better when people are looking for specific products though. They’re more enticing, thanks to the use of images.
YouTube ads
Google Ads includes some YouTube placements. These are usually pre-roll ads, which appear in the top right-hand corner of the screen, above the “Up Next” list.
Google app ads
How does Google Ads work when it comes to app campaigns? App campaigns are a bit different from other Google Ads options. If your client has a new app they want people to download, then an App campaign could be right for them. Google also allows you to target “app engagement” or “app pre-orders.”
Setting up an app campaign is also a little different. Instead of providing pre-designed creative, Google does the work. You’ll provide some text and bidding information. Google’s platform will then take that information and create the campaign for you.
Ad Rank and Quality Score
Having the biggest budget doesn’t always guarantee ad placement. Google is a little pickier, because they want to give their users the best possible experience. That means serving up relevant, high-quality ads. Answering the question "How does Google Ads work?" then, isn't just about understanding the basics but understanding the quality standards as well.
That’s why Google scores advertising campaigns on quality. It calls this program Ad Rank. A score of 10 is the highest possible quality. Google weighs a variety of factors, including how good your landing page or website is.
If you have a high-quality ad, you could outbid a high-paying competitor who has a lower Ad Rank score.
This can help you keep your client’s budget in check. You can win ad placements at lower costs, just by having a high-quality ad and website.
How does Google Ads work: How to get started with Google Ads
Getting started with Google Ads is pretty simple. Once you have a firm understanding of the question "How does Google Ads work?" then you'll want to get started by setting up your account and adding your business name. You’re ready to start creating ads.
Your next steps include setting a goal for the campaign. Google Ads can help your clients reach a wide variety of goals, whether it’s brand recognition or higher sales. A clear goal helps you keep track of performance.
Next, add your keywords to target and define your audience. You’ll usually define an audience by geographic regions. These can be broad (such as all of North America) or more granular. You could narrow your audience through the use of ZIP codes.
Finally, you’ll pick your ad types and load your creative. Select your bidding strategy, set your maximum bid, and you’re ready to submit your first Google ad.
Budgeting for Google Ads
A question you’ll likely receive from clients is how high their budget should be for Google Ads. On average, ad placements cost a little more than $2 (Investopedia).
Some keywords can have a much higher or lower cost per click, though. Specific keywords can have a lot of competition for them, which means costs increase. Broad terms can also have a lot of competition. Costs per click also vary by industry (SmartInsights).
Keep in mind that you can use different bidding strategies to help control costs. Another tip for keeping your client’s budget in check is to improve ad quality to lower costs.
Having a defined audience and good goals from the outset also helps. If a client wants brand recognition, for example, then you might opt for less competitive keywords to meet that goal. In this case, when thinking about how does Google Ads work you should consider your client's goals.
How does Google Ads work: Maximizing ad performance
How does Google Ads work? Now that you have a basic understanding, it’s time to look at optimizing ad performance. For that, you want to think about return on ad spend (ROAS).
Google says the average ROAS for Google Ads is about 8:1—you’ll earn $8 for every $1 you spend on ads. Of course, that’s an average. ROAS varies by industry, audience, campaign, and even individual ad placements.
If you want to figure out ROAS, you need to collect data. Google Ads offers tracking through Urchin Tracking Modules (UTM). You’ll want to set these up at the campaign level. You’ll also need to turn on conversion tracking to keep an eye on performance.
Tracking ROAS is simple if you have a goal like “increase sales.” If your goal is brand recognition, it may be more difficult to measure returns in a direct way. You may need to use measures such as clicks, website traffic, or even something like email sign-ups as indicators.
There are many ways to improve ROAS for Google Ads for local businesses. The tips below will help you choose better keywords and design more effective ads. That way, your clients will get more out of Google Ads campaigns.
Tip #1: Choosing the right keywords
Keyword selection is crucial to both ROAS and Google Ads success.
A good tip is to choose narrow search terms instead of broad terms. It might be tempting to target “running shoes” if your client sells running shoes. This is a broad term, though, and there will be plenty of competition for it. More competition generally means higher costs for placements, which drives down ROAS.
Narrower terms also help you home in on an interested audience. If someone in LA searches “running shoes” and your client has a shop in New York, this user probably isn’t your target audience. “Best running shoes NY” or “running shoe shops Brooklyn” might be better keywords.
No matter what keywords you select, make sure they’re relevant to your ad. If you sell running shoes, don’t target “best stilettos brooklyn.” That will frustrate users and lower your Ad Rank score.
Use a tool to plan your keywords. Google’s Keyword Planner is free and offers valuable data. You’ll see monthly search volume, competition, and ad impression share. The planner also provides low-end and high-end bids. That data can help you set your budget and even choose keywords you’re likely to get the best ROAS on.
A big part of answering the question "How does Google Ads work" comes from understanding how to choose keywords for ads.
Other tools, like PPC reporting software, can offer even more insights.
Understand match types
Another tip for ad performance is to use the different match types effectively. Google Ads offers four “match” selections:
- Exact match, where the user search matches your exact keyword
- Broad match, which “matches” your ad with any word within your keyword phrase
- Modified broad match, which lets you choose “locked-in” words with a +
- Phrase match, which matches your keyword phrase in its exact order but can include other words
Let’s look at an example of match types. Suppose a client wants to rank for “running shoe shops.” The broad match setting would allow their ad to run on searches for this phrase but also the searches “running,” “shoe,” and “shops.” An exact match would only allow the ad to run on “running shoe shops” but not even “running shoes shop.” It would have to be matched exactly.
Modified broad match could let you lock in the word “running,” but the ad may show up with phrases like “running a 5k” or “running how to get started.” A phrase match, on the other hand, lets the ad run for searches like “best running shoe shops,” “running shoe shops near me,” or even “Nike running shoe shops.”
There are also negative keywords to consider. These are words you don’t want to rank for. In our running shoe shop example, we may not want to rank for “Nike.” One, it has high costs, and two, our client doesn’t even carry Nike shoes. We’d want to add “Nike” to our negative keywords then. If someone searches “Nike running shoes,” our client’s ad won’t run.
Tip #2: Using dynamic ads
Google Ads offers other powerful tools to help you drive higher ROAS for your clients. One of those is dynamic ads.
Dynamic ads have automatically changing creative. This allows them to adjust to different users. A common example is ads adjusting for mobile versus desktop users. The platform adjusts which ad the users see using artificial intelligence (AI).
The AI does more than adjust for screen size though. It also collects data to determine which version of the ad is most likely to be effective for a given user. Google Ads calls these responsive search ads.
With responsive search ads, you can enter up to 15 headlines and four variations on your ad copy. Machine learning then tracks performance over time. It uses this information to determine the best products or services to advertise to a user.
Responsive ads effectively auto-test your ad until you find the best version. If making 15 different headlines sounds like a lot of work, though, check out automated ads. This service not only helps generate ad creative—it can help your clients advertise across digital ad platforms too.
Tip #3: The power of retargeting
How does Google Ads work when it comes to retargeting? Dynamic ads work in tandem with Google Ad retargeting. Retargeting, sometimes known as remarketing, allows you to show different ads to users who have interacted with you in the past.
When someone clicks on your ad or spends time on your website, it signals their interest. Depending on which ad they click, they may be more interested in some products than others. The platform can use that information to determine what to show the lead to get them to convert.
Retargeting can improve conversion rates, which in turn boosts ROAS. On average, a prospect needs to see your marketing seven times before they’ll convert (Kruse Control Inc). Retargeting can help you achieve that magic number while also sharing new ads that move them further along the sales pipeline.
Tip #4: Creating great ads
The very best step you can take to improve ROAS and Google Ads campaign performance is to create a great ad. As mentioned, Google uses Ad Rank to help determine winning bids.
Improving a campaign’s Ad Rank can help improve its performance. Google offers the Quality Score tool to help you keep tabs on your ads. It measures three things:
- Relevance of your ad to user searches
- Landing page quality
- Expected click-through rate (CTR) (Google)
You can’t control the expected CTR, but you can ensure your ad is relevant to the keywords you’re targeting. You can also improve the landing page experience for users.
Keys to improving an ad’s quality score include knowing your audience. Who are they? What are they likely to click on? Younger users, for example, respond better to ad copy that makes use of emojis.
Dynamic ads and testing can help here. Dynamic ads show you which ads have the best CTRs.
Of course, nothing replaces a great headline. Good examples usually include the keyword or search phrase in the headline. The better your ad copy matches their search, the more likely they are to feel like clicking your ad is a good idea.
Try to avoid clickbait headlines. These headlines often frustrate users, so they can actually decrease your quality score.
Finally, think about which type of ad campaign you should run. Knowing your audience is key here too. Is search the best place to find your client’s target audience? It might not be. In fact, they might be more likely to see your ad on YouTube.
Tip #5: Power insights with data
How do you know an ad is performing? How do you know if your conversion rate is any good? The answer is to ensure you’re getting the data you need.
You can synchronize Google’s own Analytics tools with your Google Ads campaigns. In turn, your clients can see the data. Where are clicks coming from? What devices are people using, and which screens should the client design ads for?
Data can provide powerful insights into the audience and their behavior. In turn, your client can use it to refine their ads and keyword selection. This allows the client to tweak campaigns for optimal performance.
You should keep a close eye on campaign performance, even when you’re achieving targets. Is there a way to improve performance even more? Is there a target audience that the current ad doesn’t appeal to? Data can provide answers to these questions.
As good as Google’s own analytics are, there are other programs that can give your clients more. PPC reporting software, for example, can automate reporting. That, in turn, cuts down on overhead. Some software, like Advertising Intelligence linked above, can enable your clients to generate reports across locations. They can also collect data across platforms to get a broader view of campaign performance. Not only can PPC reporting software help you provide data to clients but it can also help those clients understand how does Google Ads work too.
Google Ads is a smart investment for your clients
You’ve been pondering, “How does Google Ads work?” Now you not only have the answer to that question but a guide to help you maximize campaign performance.
Offering Google Ads and other digital advertising options is a smart move in the online era. With the right strategy and technology behind them, your clients can realize all the benefits of digital ads.