Most businesses are investing in AI, but few are getting the results they expect. That’s where AI prompt engineering comes in. Prompt engineering is the art of structuring the right instructions, context, and data so your AI produces outputs that are accurate, relevant, and usable.
When your team learns how to write effective prompts, your AI-powered workflows, from lead qualification to content creation, become faster, smarter, and far more consistent.
Here’s the challenge: most businesses are still treating AI like a magic box instead of a team member. They feed it generic commands and hope for the best.
Meanwhile, their competitors are engineering AI employees; intelligent, trained assistants who understand their brand voice, data, and goals, to deliver repeatable, high-quality results.
With the right AI marketing strategy, your business can do the same.
In this guide, you’ll learn what prompt engineering really means, why it matters for your business, and how to create powerful, structured prompts that help your AI Employees perform at their best.
Automate the entire customer journey from first touch to repeat business
TL;DR
- AI prompt engineering is the process of crafting precise, structured inputs that help AI generate better, more consistent outputs.
- Businesses that master prompting can transform AI into a true employee, handling tasks from lead capture to customer engagement with confidence and accuracy.
- Vendasta’s AI Employees use prompt engineering, your data, and automation to streamline marketing, sales, and operations across the entire SMB customer journey.
What Is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering is the process of crafting clear, structured instructions that guide an AI model to produce the output you actually need.
It’s how you turn a general-purpose AI into a purposeful one, whether that means writing a marketing email, generating a lead response, or managing a customer conversation.
AI prompting is the input you give the AI. It tells the model what to do, how to do it, and what success looks like. Strong AI prompts typically include:

- Context: What the AI needs to know before responding.
- Instructions: The exact task or goal.
- Tone and Style: How the output should sound.
- Examples: References or sample responses that model the desired format.
When done well, prompt engineering transforms AI from a “tool that guesses” into an AI employee that performs.
Why Prompt Engineering Matters for Your Business
Every AI model, whether from OpenAI, Google, or Anthropic, responds differently based on how it’s prompted.
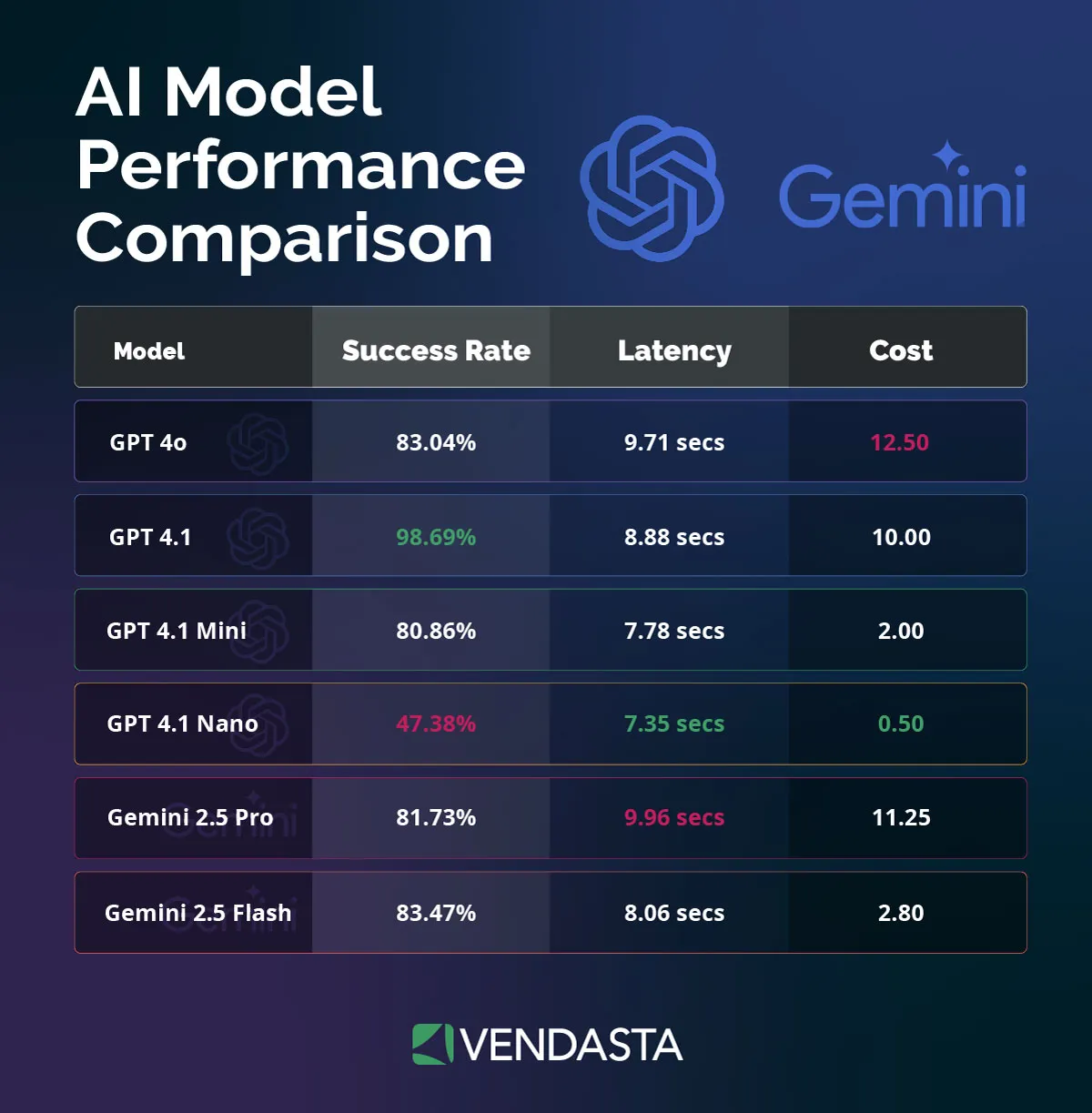
The same request can yield wildly different results depending on how it’s phrased or structured. That means the prompt is as important as the model itself.
The better your AI understands your industry, tone, and goals, the more value it delivers.
- For a marketing agency, it can mean AI-generated campaigns that match your client’s brand voice.
- For a franchisor, it can ensure every location uses consistent messaging.
- For an MSP, media company, or ISV, it can automate routine communication while maintaining quality and accuracy.
- For the SMB, it means faster, smarter, and more personalized service, from instant replies to tailored marketing and customer support that feels human.
In short, prompt engineering helps your AI act less like a chatbot and more like a trained employee, one who knows your processes, understands your customers, and speaks your language.
How Major Providers Define Prompt Engineering
While each AI provider explains it a little differently, the concept is consistent across the industry:
- Google Cloud defines prompt engineering as “the art and science of designing and optimizing prompts to guide AI models toward desired outputs.”
- AWS describes it as “the process where you guide generative artificial intelligence (generative AI) solutions to generate desired outputs.
- OpenAI calls it “writing effective instructions for a model, such that it consistently generates content that meets your requirements.”
The takeaway? Every major AI leader agrees: how you write your prompt determines what you get back.
The Key to Unlocking Your AI Employees’ Potential
When paired with Vendasta’s AI Employees, prompt engineering becomes even more powerful.
Each AI Employee is built with the intelligence to use your business’s data, automate workflows, and engage customers just like a trained team member. But the quality of their work still depends on how you prompt them.
Using structured prompts helps your AI Employees:
- Pull accurate information from your knowledge base.
- Follow your business rules consistently.
- Communicate in your brand’s tone and personality.
- Deliver faster, more relevant results for your SMB clients.
Prompt engineering is the bridge between generic AI outputs and tailored business performance. It’s the skill that separates those experimenting with AI from those scaling it across their entire customer journey management.
How Prompt Engineering Works: Step-by-Step Guide for Your Business
To make AI truly useful, you need more than a clever command. You need a structured framework for writing prompts that your AI can reliably interpret and act on.
Whether you’re using AI for lead scoring, managing customer chats, or generating marketing content, the process follows the same principles.
Here’s how to build prompts that help your AI employees think and respond like trained members of your team.
Step 1. Define the Objective
Before writing any prompt, start with the end in mind. What do you want the AI to accomplish, and how will you measure success?
For example:
- Are you trying to generate a blog post for a client’s local campaign?
- Do you want to collect lead information from a website visitor?
- Or are you prompting your AI receptionist to book appointments and handle FAQs?

Your objective sets the direction for everything else. The clearer the goal, the more precise your results will be.
Pro Tip: In Vendasta’s AI Employee setup, begin with a purpose prompt that clearly states the employee’s role, tone, and desired behavior. This is the foundation of reliable AI marketing automation.
Step 2. Provide Context and Examples
AI performs best when it understands the situation it’s responding to. Add background information that helps it generate outputs aligned with your brand and audience.
Include details such as:
- The type of business or industry (e.g., dental clinic, landscaping company, or auto shop).
- The target audience (e.g., local homeowners, business owners, or franchise partners).
- Tone and communication style (e.g., friendly and helpful, professional and concise).
Whenever possible, use few-shot prompting, showing one or two examples of the output you expect. This technique helps the AI learn your preferred structure and voice faster.
Step 3. Craft The Prompt Format
The way you format your prompt determines how clearly the AI understands your instructions. A structured format reduces confusion, ensures a consistent tone, and gives you more control over the output.
Start with clear, explicit instructions, then layer in context, examples, and any constraints, such as word count or tone.
According to OpenAI’s Help Center, placing instructions at the beginning helps the model anchor its understanding before it processes the rest of the input.
Why Formatting Matters
AI models don’t read like humans. They analyze patterns in your text to infer structure and meaning.
When your prompt includes well-defined sections, labeled elements, or visual cues, it’s easier for the model to interpret each part correctly.
Good formatting also makes prompts easier to reuse, edit, and scale across multiple business cases.
Use Delimiters To Organize And Clarify
Delimiters are visual markers that separate different parts of a prompt. They act as signposts, indicating where one idea ends and another begins. Without them, the AI may blend unrelated instructions or ignore details.
Here are the most common delimiters and their purposes:
| Delimiter | Example In Use | Purpose |
| Quotation Marks (“ ”) | You are an AI writer. Always “respond in a friendly tone that builds trust.” | Define direct instructions or emphasize a specific phrase. Helps the AI recognize the quoted text as something to follow verbatim. |
| Triple Quotation Marks (“””) | Provide an example for tone: “””Here’s an example of the ideal output format: ‘Need reliable repairs? Book with Handy Helper today!’””” | Separate long examples or structured text, such as sample messages, email templates, or tone examples. Keeps the AI from blending sample text with instructions. |
| Triple Backticks (“` ) | You must use this format: “`Heading: [Blog Title] Paragraph: [Intro text, 2–3 sentences] Bullets: – [Key Point 1] – [Key Point 2]“` | Indicate code blocks, structured output, or formatting boundaries. Everything between the opening and closing triple backticks is treated as one section, which is ideal for showing templates or layouts you want the AI to replicate. |
| Hashtags (#, ##) | # Purpose
You are an AI marketing assistant. ## Tone Friendly, confident, and professional. |
Create readable headings that act like “sections” for the AI. Helps structure the prompt like an outline, making it easier for the model to parse intent. |
| Square Brackets [ ] | Write a 200-word blog for [CLIENT NAME], a [INDUSTRY] business based in [LOCATION]. | Use placeholders for dynamic data that changes per use case, like client names, industries, or regions. Makes prompts reusable across projects. |
| Curly Braces { } | If the user provides a postal code, {verify the service area before giving a quote}. | Define conditions, constraints, or dynamic elements inside logic-based prompts. Tells the AI to act only when a condition is met. |
| Colons (:) and Hyphens (-) | Tone: Professional and concise.
– Include 3 actionable takeaways. – End with a clear CTA. |
Help the AI interpret lists, attributes, or key parameters. Colons define properties; hyphens signal list items or step-by-step actions. |
Example 1: A Well-Structured Marketing Prompt
# Purpose
You are an AI content strategist for small business marketing partners.
# Task
Write a 300-word blog post about SEO best practices for local retailers.
# Instructions
- Use a friendly, professional tone.
- Include 3 actionable tips and a clear call-to-action.
- Reference relevant Google ranking factors.
# Example
“””SEO can seem complex, but small changes often have the biggest impact…“””
Why it works:
- The hashtags create clear sections that the AI can follow.
- Bullet points define requirements precisely.
- The triple quotes isolate a sample paragraph, teaching tone, and structure.
Example 2: Customer Support Prompt Using Backticks And Brackets
You are a customer support assistant for a home repair service.
When a customer asks about scheduling, respond using this format:
“`Greeting → Confirmation → Link to schedule.“`
Example Input: “Can I book an appointment for next week?”
Example Output:
“Sure! I can help with that. You can book a visit at [BOOKING_LINK].”
Why it works:
- The backticks tell the AI where examples and instructions begin and end.
- The brackets create placeholders for dynamic content like URLs or client data.
Example 3: Conditional Instructions With Curly Braces
If the user provides a postal code, {verify the service area first}.
If the area is valid, {offer a quote and appointment options}.
Always end with a friendly closing message.
Why it works:
- The curly braces highlight key actions or conditional logic.
- Each condition is separate and clear, preventing the model from skipping steps.
Best Practices For Structuring Prompts
- Lead with purpose: Begin with a role or goal (“You are a…”) to set the frame.
- Group logically: Keep related details (like tone, structure, or examples) together.
- Separate each function: Use delimiters to avoid overlapping concepts.
- Be explicit: Don’t assume the AI “knows” what you mean. Spell out instructions.
- Keep it readable: Well-formatted prompts are easier to maintain, share, and refine.
Step 4. Test And Iterate
No prompt is perfect on the first try. Once you’ve written one, test it, review the output, and adjust until the results are consistent.
Ask questions like:
- Does this output meet my tone, length, and structure requirements?
- Is it factually accurate and aligned with the goal?
- Does it sound natural and human?
An iterative approach is key. Small refinements can dramatically improve reliability. Adjust instructions, tighten constraints, and add missing context until your output consistently hits the mark.
Step 5. Scale And Operationalize With A Prompt Library
When you find prompts that work, save them. A well-organized prompt library helps your business scale AI use across teams and clients.
Create categories such as:
- Marketing Prompts: Blog posts, emails, ad copy, social media
- Sales Prompts: Follow-ups, lead nurturing, proposal summaries
- Support Prompts: FAQ responses, service confirmations
Each prompt should include:
- The intended task and use case
- Expected output format
- Sample results for reference
Maintaining version control and performance tracking ensures consistency as your AI systems evolve. This is especially valuable for agencies or franchisors serving multiple SMB clients—reusable prompts save time while preserving brand quality.
Pro Tip: To jump-start your library, download Vendasta’s free ebook, 100 AI Prompts Every Marketer Needs. It’s packed with ready-to-use prompt templates that can help your team accelerate marketing tasks.

Step 6. Monitor, Measure, And Refine
Prompt engineering is never “set it and forget it.” Regularly review and measure how your prompts perform.
Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as:
- Quality of output: How often does it require human editing?
- Efficiency: How much time does each task save?
- Impact: Are clients more satisfied or engaged as a result?
If accuracy drops or model behavior changes, revisit your prompts. Update instructions, clarify examples, or refresh contextual data. Over time, this creates a feedback loop that makes your AI smarter and more dependable.
Prompt Engineering Techniques Your Business Should Use
Below is a breakdown of the most effective prompt engineering techniques your business can start using today.
Each one can be applied to marketing, sales, or operational workflows to boost productivity and consistency.
| Technique | What It Does | When Your Business Uses It |
| Zero-Shot Prompting | Gives the AI a single, direct instruction with no examples. The model uses general training data to infer what you want. | Use for quick, low-complexity tasks where the goal is simple and predictable. For example, generating a social post or summarizing a meeting note. |
| Few-Shot Prompting | Includes one to five examples to show the AI the format, tone, or type of response you expect. This helps it learn patterns and replicate them. | Use for medium-complexity tasks like writing blog posts, ad copy, or client emails where tone and structure matter. |
| Chain-of-Thought (CoT) | Instructs the AI to “think step by step” or explain its reasoning before giving the final answer. This improves accuracy on logical or analytical tasks. | Use for complex reasoning tasks such as report generation, ROI analysis, or marketing strategy recommendations. |
| Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) | Allows the AI to pull information from external data sources, like documents, websites, or CRMs, before generating an answer. | Use when accuracy and brand alignment are essential, such as creating client proposals, referencing product specs, or answering FAQs using your business’s data. |
| Role-and-Persona Prompting | Assigns a specific role or identity to the AI (e.g., “You are a marketing director for a local franchise”). This sets the tone, perspective, and voice. | Use when your output must reflect a specific point of view or audience, like brand storytelling, customer communication, or sales enablement materials. |
| Constraint/Structure Prompting | Defines the format, tone, and structure (e.g., “Write 200 words in paragraph form with three bullet points and a call-to-action”). | Use for deliverables that require precision and formatting, such as newsletters, web copy, or proposals. This ensures outputs are ready for client review. |
Applying These Techniques In Your Business
The key to success is knowing when to combine techniques. For example:
- Pair role prompting with a few-shot examples to create consistent blog posts across multiple clients.
- Use Chain-of-Thought reasoning with RAG when your AI needs to analyze internal sales data before making recommendations.
- Combine constraint prompting with persona context to produce branded content that aligns with client tone and style.
Start small by testing one technique per task, then layer additional ones as your team gains confidence. Over time, you’ll build a prompt framework that adapts to any workflow.
How To Prompt Your AI Employees
TL;DR
- Prompting your AI Employees is about structuring context, conditions, and goals so they act like real team members.
- Use Markdown formatting, logical order, and clear instructions to help AI Employees interpret tasks the same way humans would.
- Vendasta’s AI Employees respond best when you balance capabilities (instructions), knowledge (facts), and tools (actions).
What Makes Vendasta’s AI Employees Unique
Vendasta’s AI Employees are not simple chatbots. They’re configurable, data-aware digital team members that help attract, engage, and support SMB customers across the entire customer journey.
They combine automation, intelligence, and personalization to deliver meaningful business outcomes and facilitate AI business transformation.
Every AI Employee operates using three fundamental components that work together:
- Knowledge: The factual foundation that the AI references to provide accurate answers, such as documents, website content, or structured data.
- Capabilities: Behavioral instructions that define how, when, and why the AI Employee should act or respond.
- Tools: System integrations (like CRMs, schedulers, or email senders) that allow the AI to take real actions instead of simply responding.
Pro Tip: In the Knowledge Base Optimization session, Jon Neher emphasized that effective prompting happens when you combine all three correctly. Trying to encode everything into one giant prompt creates confusion and inconsistency. Instead, let knowledge handle facts, capabilities handle logic, and tools handle execution.
Watch the complete session here:
Step 1. Define The Purpose Prompt – Set The Frame At The Top
Every AI Employee begins with a purpose prompt. This is the foundation of its personality, tone, and role. This section sets the “frame” that shapes how the AI interprets all future instructions.
In other words, what you write first defines how your AI Employee sees its purpose.
When crafting your purpose prompt:
- Open with a clear mission. Example: “You are an AI receptionist for a home-repair business.”
- Define tone and brevity. Keep it conversational and on-brand for your business.
- State behavioral goals. Clarify what success looks like for each interaction.
Example:
# Purpose
You are an AI receptionist for a small business.
Always greet politely, confirm the service area, and collect lead details before giving quotes.
This section ensures every conversation begins with the right voice, clarity, and consistent behavior.
Step 2. Use Markdown Formatting To Help Your AI Employee “Read”
AI models interpret structured text similarly to how humans scan a page. By using Markdown formatting, you help the AI understand hierarchy and intent.
Use:
- Headings (#, ##) to define sections like Purpose, Conditions, or Examples.
- Bold and capitalization sparingly to emphasize important rules.
- Short, readable lines that follow a logical order.
Example Structure:
# Purpose
# Conditions
## Collect lead details first
## Only quote after postal code
Readable, labeled sections make troubleshooting easier later. If your AI Employee ever misbehaves, you’ll know which rule to adjust.
Step 3. Build Logic With “If/When/Before” Conditions
Prompts aren’t static—they can represent logic and decision-making. Using conditional language like if, when, before, or after turns your prompt into a dynamic workflow.
Conditions create clarity and control, helping your AI follow business logic even when conversation styles vary.
Example:
If the user asks about a service,
THEN verify postal code before quoting a price.
WHEN postal code is valid,
provide diagnostic fee and appointment options.
Conditional statements connect capabilities, such as lead capture → service area verification → diagnostic fee generation.
Following this approach ensures your AI behaves predictably and reliably across interactions.
Step 4. Place Important Actions Strategically (Top vs. Bottom)
Large Language Models (LLMs) follow a top-to-bottom reading order. The structure of your prompt impacts how well the AI prioritizes different instructions.
The order of content affects behavior:
- The top sections set the context and role.
- Middle sections define rules and logic.
- Bottom sections are where the model most closely follows specific instructions.
Writer Guidance:
- Put key behavioral framing (role, personality, purpose) at the top.
- Place output or action-based instructions at the bottom (e.g., “only provide diagnostic fee after postal code”).
- Use the middle section for context and examples.
Step 5. Balance Determinism And Natural Conversation
Prompting is about creating a natural user experience. That means balancing deterministic (rule-based, predictable) and non-deterministic (creative, conversational) behaviors.
Deterministic flows work best for:
- Compliance-driven interactions (quotes, booking, data capture).
- Processes that need accuracy and consistency.
Non-deterministic flows shine in:
- Human-like conversations.
- Greetings, small talk, or empathetic responses.
Guidance:
- Use deterministic prompts for structured workflows like qualification or billing.
- Allow flexibility in casual exchanges to keep interactions engaging.
- Test your conversations using Vendasta’s Conversations AI to review what knowledge sources were used and how well the model followed conditions.
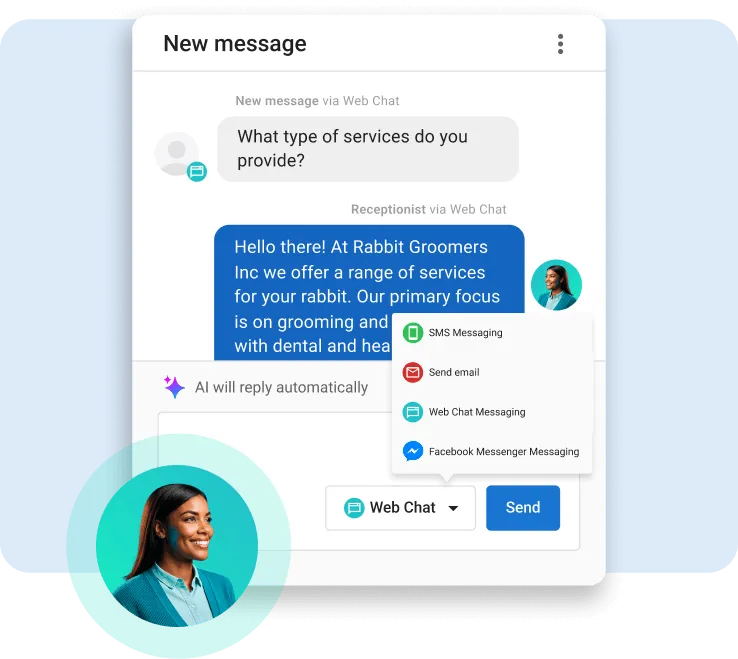
Step 6. Combine Knowledge, Capabilities, And Tools Effectively
Each AI component serves a different purpose. Combining them properly unlocks your AI Employee’s full potential.
- Knowledge provides information: product details, FAQs, or company policies.
- Capabilities control behavior: when to answer, what to prioritize, or how to respond.
- Tools perform actions: booking appointments, sending messages, or retrieving CRM data.
Writer Guidance:
- Keep facts inside your Knowledge Base, not inside prompts.
- Keep behavioral logic inside capabilities.
- Let tools handle real actions.
Example Flow:
Knowledge: Service pricing CSV, business hours.
Capability: “When the user asks for an estimate, use knowledge to provide a price range. If the user is ready to book, trigger the scheduling tool.”
This layered approach keeps your AI scalable, organized, and easier to maintain as your client base grows.
Step 7. Optimize And Test Your AI Employee
Prompting is iterative. Each test helps you refine your AI Employee’s accuracy, tone, and efficiency.
Testing Workflow:
- Run conversation flows in Vendasta’s Conversations AI to simulate real user interactions.
- Review logs to see which knowledge sources were triggered.
- Adjust prompts or knowledge if the AI references outdated or irrelevant information.
- Refine logic when conversation paths break or produce inconsistent responses.
Jon Neher’s insight still applies: “More modules mean more potential for error—start small.” Build a solid foundation before scaling capabilities.
Pro Tip: Keep a version history of your prompts. Label each change and track performance improvements over time. This ensures you can measure progress and roll back if needed.
Practical Checklist For Prompting Your AI Employees
| Area | What To Check | Why It Matters |
| Purpose Prompt | Defines tone and role. | Sets the conversation frame and voice. |
| Markdown Structure | Clear headings and bolded rules. | Improves AI readability and organization. |
| Conditions (If/When/Before) | Logical flow and dependencies. | Prevents broken or inconsistent conversation loops. |
| Placement (Top vs. Bottom) | Order of framing vs. instruction. | Maximizes adherence to key rules. |
| Determinism Balance | Predictable logic vs. human tone. | Keeps responses natural while maintaining control. |
| Knowledge-Capability Separation | Facts vs. instructions. | Reduces confusion and hallucinations. |
| Continuous Testing | Review AI explanations and outputs regularly. | Improves reliability, accuracy, and user satisfaction. |
Pro Tip: If you want a deeper dive into prompt logic, knowledge optimization, and real-world examples of how AI Employees are built inside Vendasta, watch the full webinar here:
AI Prompt Engineering Training
Building effective AI workflows happens through experimentation, learning, and the right guidance.
For partners who want to master prompt engineering and put AI to work across marketing, sales, and operations, Vendasta’s Build Mode series is the place to start.
Hosted by Jon Neher, Build Mode is a live, hands-on webinar series designed to help you learn how to prompt, train, and deploy AI Employees that work like real members of your team.
Each session walks through practical examples and best practices drawn directly from Vendasta’s platform.
What You’ll Learn
Each Build Mode session focuses on how to design, optimize, and manage AI workflows for your business and your SMB clients. Topics include:
- Prompt structure and design: How to write purpose prompts, organize logic, and use Markdown formatting effectively.
- Knowledge optimization: How to build, clean, and structure data so your AI Employees can access accurate information.
- Conditional logic and workflows: How to chain actions, apply “if/when/before” logic, and build reliable task sequences.
- Testing and troubleshooting: How to review conversation logs, refine responses, and continuously improve accuracy.
These sessions demonstrate how to turn your prompts into operational results.
Ready to level up your team’s AI skills? Catch up on the latest episodes anytime in our on-demand library.
Sign up for the live sessions here.
Watch the replays on YouTube here.
Each episode is packed with actionable insights you can apply right away to make your AI Employees smarter, faster, and more reliable.
AI Prompt Engineering FAQs
1. What Is AI Prompt Engineering?
AI prompt engineering is the process of designing structured inputs that guide an AI model to produce accurate, useful, and brand-aligned results. It helps your business get consistent outputs from AI tools, especially when creating marketing content, reports, or customer responses.
2. Why Does Prompt Engineering Matter For My Business?
Strong prompt engineering turns generic AI tools into tailored assistants. For partners using Vendasta, effective prompting ensures AI Employees deliver responses that match your brand voice, improve customer interactions, and automate work without losing quality.
3. How Does Prompt Engineering Improve AI Accuracy?
When you give clear instructions, context, and examples, the AI interprets your intent more precisely. Structured prompts reduce errors, limit irrelevant outputs, and help the model focus on producing responses that align with your goals and audience.
4. Do I Need Technical Skills To Learn Prompt Engineering?
No. You don’t need to be a developer. Anyone can learn prompt engineering by following best practices, such as defining objectives, adding context, and testing results. Vendasta’s Build Mode webinars make it simple with real-world examples and templates you can use immediately.
5. How Is Prompt Engineering Used With Vendasta’s AI Employees?
Vendasta’s AI Employees use prompt engineering to combine capabilities, knowledge, and tools. This structure lets them act like real team members, responding to customers, booking appointments, or generating marketing content based on your business’s data and brand tone.
6. What Are The Best Prompt Engineering Techniques To Start With?
Start with few-shot prompting (show examples), role prompting (define the AI’s persona), and constraint prompting (set word count and tone). These methods are simple to learn and deliver reliable, repeatable results for most marketing and operations tasks.
7. How Can I Train My Team On AI Prompting?
Your team can learn through Vendasta’s Build Mode webinar series hosted by Jon Neher. Each session covers how to write, test, and refine prompts that help AI Employees perform complex workflows across marketing, sales, and support.
8. What’s The Difference Between Prompt Engineering And AI Training?
Prompt engineering teaches you to guide existing AI models effectively. AI training, on the other hand, involves updating or fine-tuning a model’s data. With Vendasta, you don’t need to train models—prompting and knowledge optimization handle most customization.
9. Can Prompt Engineering Help My Agency Or Franchise Scale?
Yes. Once you create reusable prompt templates, you can apply them across multiple clients or locations. Vendasta’s platform supports this by letting partners deploy consistent, branded AI workflows across campaigns, service chats, and lead capture processes.
10. Where Can I Learn More About AI Prompt Engineering?
You can explore practical tutorials and live examples in Vendasta’s Build Mode series. Start with Build Mode: AI + Ops in 30 or access the full on-demand library at vendasta.com/build-mode.

